1. Definition
An identifier is a unique association between an alphanumeric code and an entity or a ressource. On the web, ressources are located by URLs. However, these URL's are not stable. If the resource is moved and/or renamed, it is no longer accessible. The browser then displays the 404 error code. Persistent identifiers guarantee a stable link to the online resource. The persistency is obtained by an active management of URLs.
This management is ensured by recognized organizations, support by human and technical infrastructures. The identity of the resource is matched to its location on the web. The hypertext link access will be guaranteed and will never be broken.
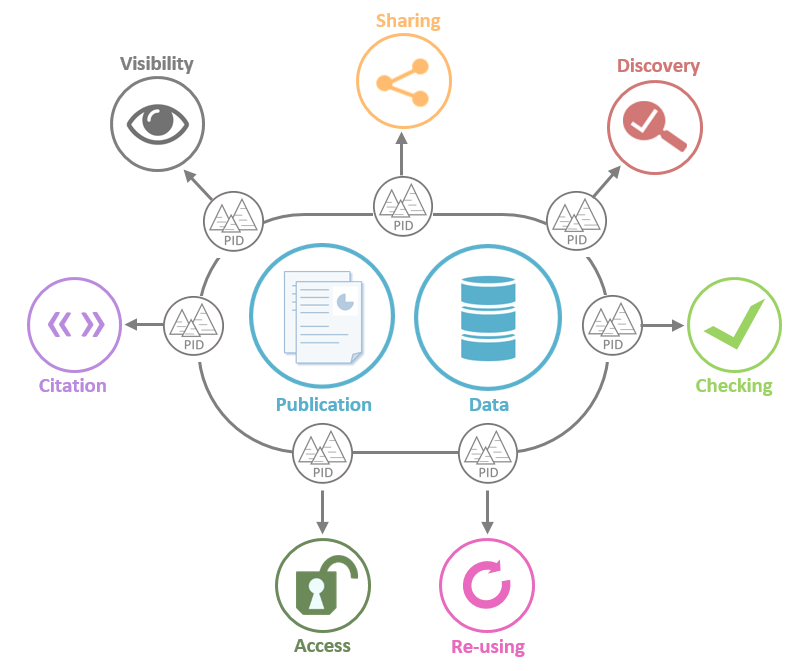
The role of persistent identifier is to facilitate the tracking, to locate, access and cite the results of research production:
- Persistent identifiers allows a sure identification (to a resource, an author...).
- Persistent identifiers for publications and data allow to access them over the long term.
- They link published articles to the underlying data sets.
- They also help to discover, share, reuse and cite the results of research and scientific production.
Source :
Doranum - Persistents identifiers
The ideal identification is a combination of several identifiers:
- PID for publications
- PID for data
- PID for authors
- PID for research organizations
 Source
Source :
Doranum - Identifiants pérennes : FICHE SYNTHÉTIQUE
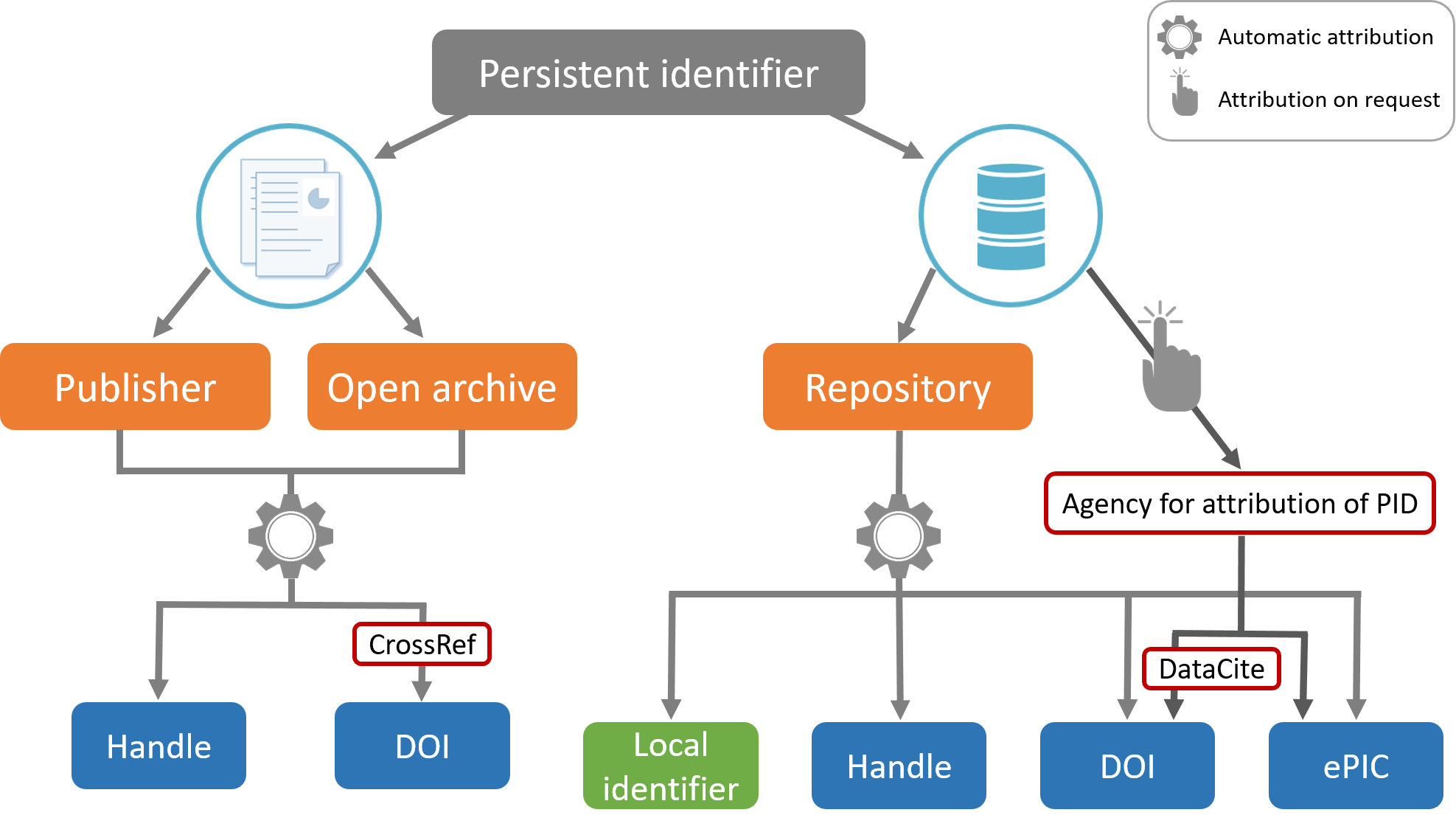
For publications, the attribution of a perennial identifier is a well-established and systematized procedure. Most publishers and open archives automatically assign a persistent identifier to each article. This is most often a Handle or DOI. The latter is assigned through the CrossRef agency.
Source :
Doranum - Les identifiants pérennes : un aperçu
Identifiers are often assigned to your data when they are deposited in a repository: it can be a local identifier, or a unique global identifier.
In this course, we will not talk about PID for publications.